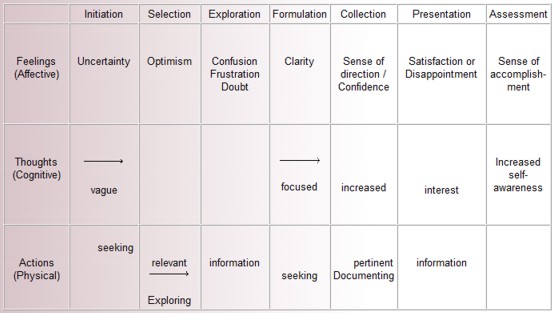
Kuhlthau, 2004.
The Year 8 immersive big picture project has come to an end. After an intense and productive week, students presented their perspective on what makes the human race worth saving with creativity and technical flair. Though the bell sounded the end of the week, the learning process, I imagine, will continue visibly and invisibly beyond the project itself.
I’ve always been more interested in the unseen learning, the mental moments and shifts in between the visible structure. Supported by a 7 day continuum, uninterrupted by regular classes, if learning moments were audible or contained in comic speech bubbles, we would have heard ‘ping!’ and ‘zap!’ and ‘kaboom!’ If learning was a visible chemical reaction, we would have seen from discussion and interaction marvellous blended colours and awesome explosions.
Watching and assessing the presentations (mainly film or photostory), a spectrum of topics and creative approaches was noticeable, as well as depth of thought and synthesis. Some of the presentations were obviously stronger, and others weaker, but sitting next to the teacher who knew the class well, I was able to glean valuable insights such as whether the student had come a long way, pushed boundaries or surprised with hidden talents. Choice and big picture questions had allowed students to connect with topics of interest, and some had run with this. If the idea behind this project (or one of them) was to engender passion-based learning, then this was successful in a good number of final products, but the architecture of learning and teaching is multi-layered, and in the aftermath, there is much to be reflected upon and pulled apart.
These are some of my thoughts throughout the week as I roamed from room to room:
- the confusion and mess at the start is normal, and should be a warning point to students and teachers
- Carol Kuhlthau’s graph of ups and downs in the affective domain during the research process may be useful to provide an insight into what can initially be a frightening undertaking
- teachers are just as much learners in this situation, and a forum throughout the process would be great support as well as make transparent the learning journey if recorded
- there was a noticeable difference between some classes in terms of concepts grasped and degree of synthesis, so teacher support in unpacking questions, leading discussion and debriefing at different stages of the process cannot be underestimated
- time needs to be taken by teachers to equip themselves for this journey
- assessment encompasses the whole process through recording in One Note and is more valuable than the assessment of just the final product
- a celebration involving the entire project cohort is an important part of the journey, and although this was done by some teachers to some degree, there was insufficient time to do this properly
- the learning process will continue silently after the last day, and we should not lose this but provide opportunities for discussion and reflection, and record these.
I’m looking forward to a recorded presentation of this journey, especially comments from students and teachers about how they felt at different stages, and what they learned along the way.

